How to Buy a 3D Printer
How to Buy a 3D Printer

The future is here: 3D printers that can build objects on need are not simply bachelor, but also affordable. This emerging area of technology offers a lot of potential, merely also many pitfalls. So, what do yous demand to know, and which 3D printer is the correct ane for you?
The first matter you will need is patience. 3D printing is an area that'south developing very quickly, just the 3D printers yous tin buy now are a long style from the replicators of Star Trek fame. They print slowly — oftentimes taking many hours to produce a single object — and they offer a limited range of materials (virtually apply ii types of plastic, called PLA and ABS).
More: Best 3D Printers
Even the best consumer 3D printers can merely build objects upwardly to the size of a loaf of breadstuff, and cheaper models have smaller build areas that usually measure only a few inches on each side. But these printers tin can create objects of surprising strength, smoothness and clarity that tin can be very useful around the domicile, ranging from custom salt-and-pepper shakers to homemade replacements for hard-to-find parts.
How 3D Printing Works
To start, you need a model of the object you want to build. This tin be a model that you make yourself in 3D-modeling software, such every bit Blender; a 3D scan of an existing object; or a model that you download from the Internet.
The software that works with the printer then takes this model and slices it, converting it into a series of thin layers that the 3D printer can impress, ane at a time. This is why some 3D-printed objects accept a stair-step look to them, formed by the layers stacked on top of one another.

How the 3D printer prints these slices to class the terminal model varies. Most consumer models are filament printers, which use a thin cord of plastic that is melted in the extruder, where the molten plastic drops onto the building surface. More-advanced (and expensive) 3D printers use a resin, and the most-expensive models utilize a powder that is melted or liquefied (and and so chop-chop hardens) to bind to the layer below it.
MORE: XYZ Da Vinci 3D Printer/Scanner Review: Mixed Results
Nearly 3D printers come fully assembled and set to print, merely some are sold equally kits that you assemble yourself. The prebuilt models are easier get-go with, merely the kits offer improve insight into how these printers work, and allow yous to customize and tweak them yourself when they are up and running. In that location are a lot of parts, simply almost kits require simply bones mechanical knowledge: If you've put together an Ikea bookshelf, y'all tin can build a 3D-printer kit.

Although 3D printers currently accept some limitations, these devices are the vanguard of a technology and design revolution in which you tin can make what you want, when you want it. Let'southward run down the different types of 3D printers and the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Types of 3D Printers
Entry-Level Filament 3D Printers
Price Range: $350 to $ane,500
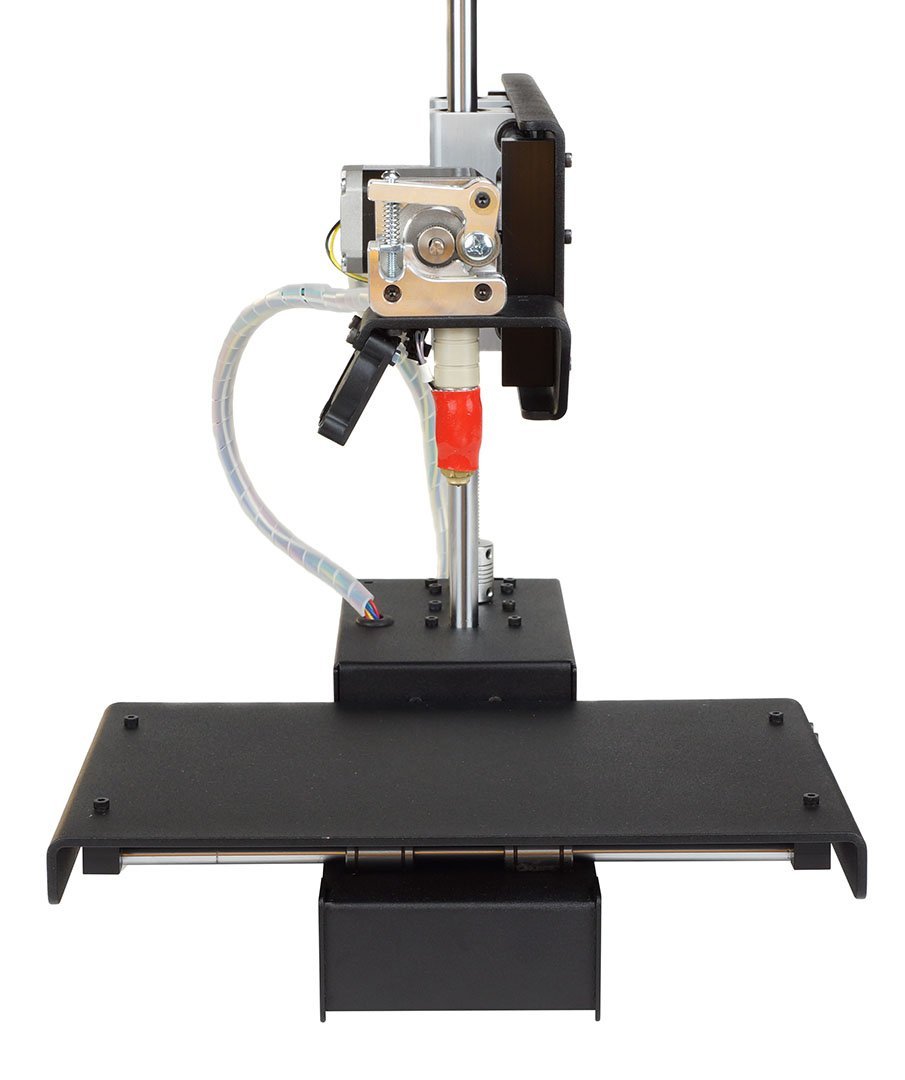

The cheapest 3D printers are simple models, similar the $749 Printrbot Simple with Heated Bed or the $999 Cubify Cube iii (see review). These printers use a process typically chosen filament deposition manufacturing (FDM). A plastic filament is melted and and so deposited in thin layers that build upwardly the model. There are two possible types of plastic: ABS, or an organic version known every bit PLA. Budget printers have a unmarried nozzle for laying down the filament.
Pros: Depression-toll, simple printers are an ideal entry betoken for 3D press. They are usually relatively straightforward to set up and configure.
Cons: This type of 3D printer prints only 1 color or cloth at a fourth dimension, and the build area is usually fairly modest — typically well-nigh 4 x 4 x 4 inches (10 10 ten x 10 centimeters).
Primal Features & Accessories: Most printers of this blazon include basic software, but some come with no software, leaving you to find open-source solutions. They typically employ 1.75 or 3mm filament, which is widely available on rolls in a range of colors.
Loftier-Stop Filament Printers
Cost Range: $1,000 to $3,000
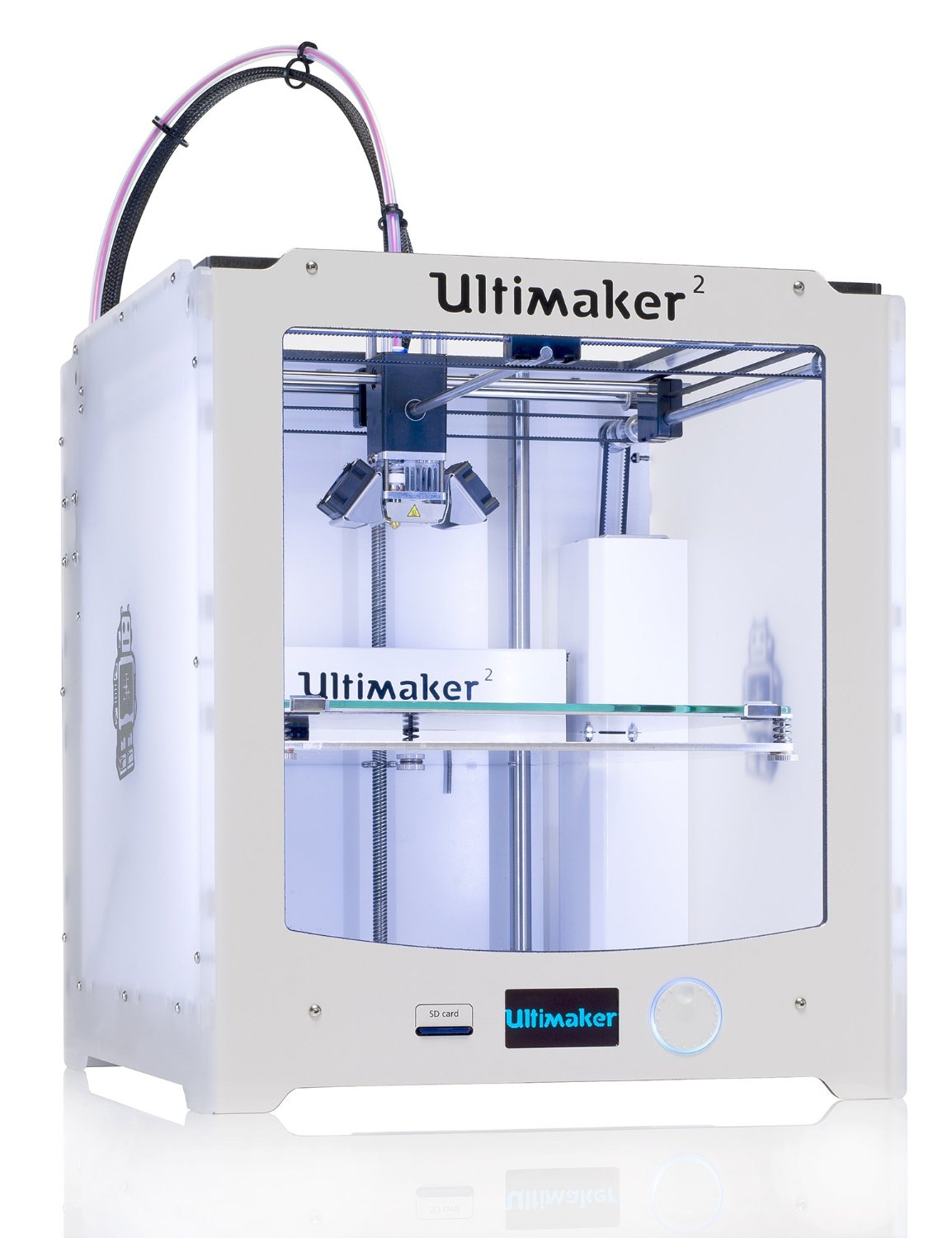

More sophisticated FDM filament printers, like the $two,500 Ultimaker 2 (come across review) or the open-source RepRap Mendel ($1,595 for a kit), add actress features to the standard 3D filament printer, such as multiple extruders and thinner layers (downwards to 0.0039 inches, or 0.1 millimeters) for smoother prints.
Pros: Larger print areas mean bigger prints than their simpler cousins tin can produce. Multiple extruders mean multiple colors or materials in ane object.
Cons: College cost. More sophisticated designs and parts can hateful more parts that could suspension with heavy use.
Key Features & Accessories: The number of extruders, either included or available as an upgrade, and the improved vertical or Z resolution are the critical factors here. These models tend to offering larger build areas, often upwards to near x x vi ten vi inches (25 x 15 x fifteen cm).
Other-material FDM 3D Printers
Cost Range: $2000 and up
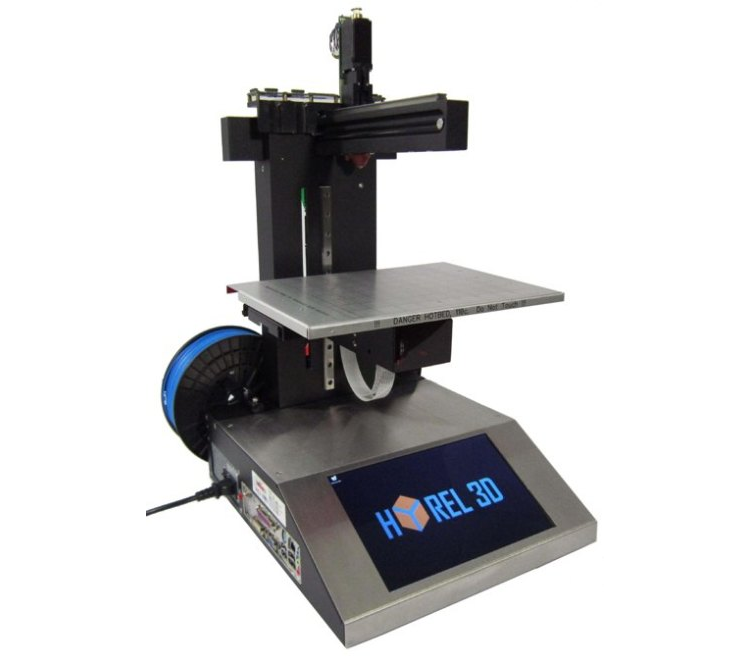

Relatively low-cost printers that tin employ materials other than plastic are commencement to appear on the market place. Hyrel offers an extruder on its E series printers — like the $i,245 E2 — that tin can print using any air-stale material, such every bit clay, Plasticine or the pop air-cured plastic Sugru. The Plasticine can be expert for producing more flexible models, and Sugru is known for its elasticity. Unlike almost printed plastics, Sugru tin can bend, stretch and flex almost like prophylactic.
Pros: Back up for press materials other than plastic means more than flexible printing in a range of materials that may be more suited to the chore at hand. You tin print pots and dishes of air-stale clay, for instance.
Cons: Back up for other materials is ofttimes experimental, then yous have to figure out what they can (and can't) do.
Key Features & Accessories: Wait for the number of extruders that the device can back up, and the toll of these and other extras that might be needed for your materials.
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printers
Toll Range: $3000 and upwardly
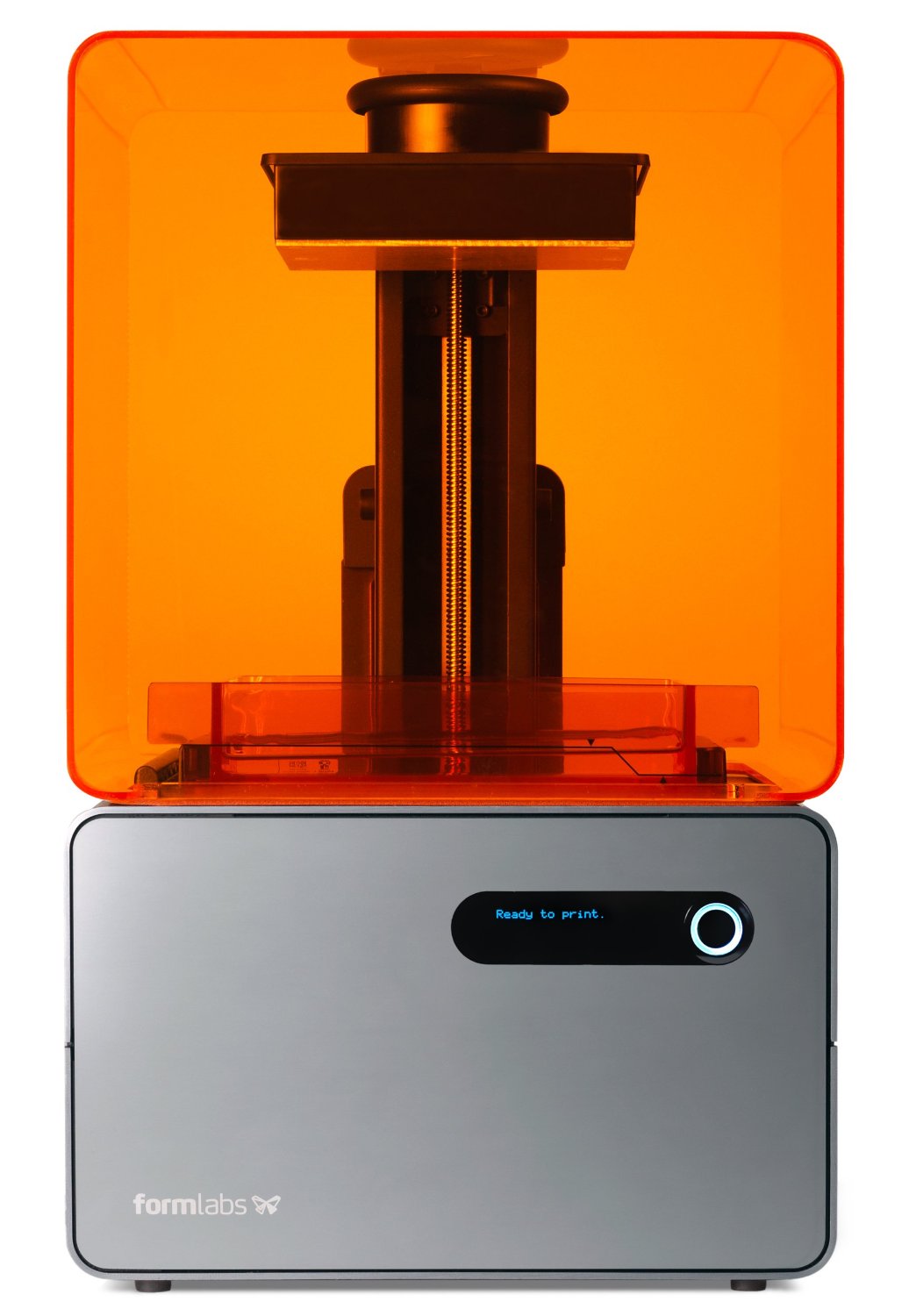

New on the 3D printer market are models chosen Stereolithographic or SL printers, like the $3,299 Form 1+ (see review) or the B9Creator ($2,990 kit, $iv,995 assembled), which use a photosensitive resin and a digital projector or light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The light is shone on the resin in the pattern of the layer, causing it to solidify. The build surface is then lowered, and the calorie-free forms another layer until the object is complete. These printers can produce very-high-resolution objects, but the colors of the resin are express.
Pros: Very loftier resolution, shine prints, with details every bit fine every bit 0.012 inches (0.030 cm) and layers as thin as 0.001 inches (0.003 cm). The printing process is usually quicker than with FDM filament models.
Cons: Limited range of resin colors, and the newness of the technology makes both the printer and the print resin expensive.
Key Features & Accessories: The toll of the printer and the types of resin are the key considerations: For the Form 1+, the resin currently costs $149 per liter, and is bachelor in only clear, white, gray and blackness. The build area is also a critical characteristic to consider; most offer minor build areas of most half dozen x five x 5 inches (15 by 13 by 13 cm).
Powder 3D Printers
Price Range: $10,000 and up
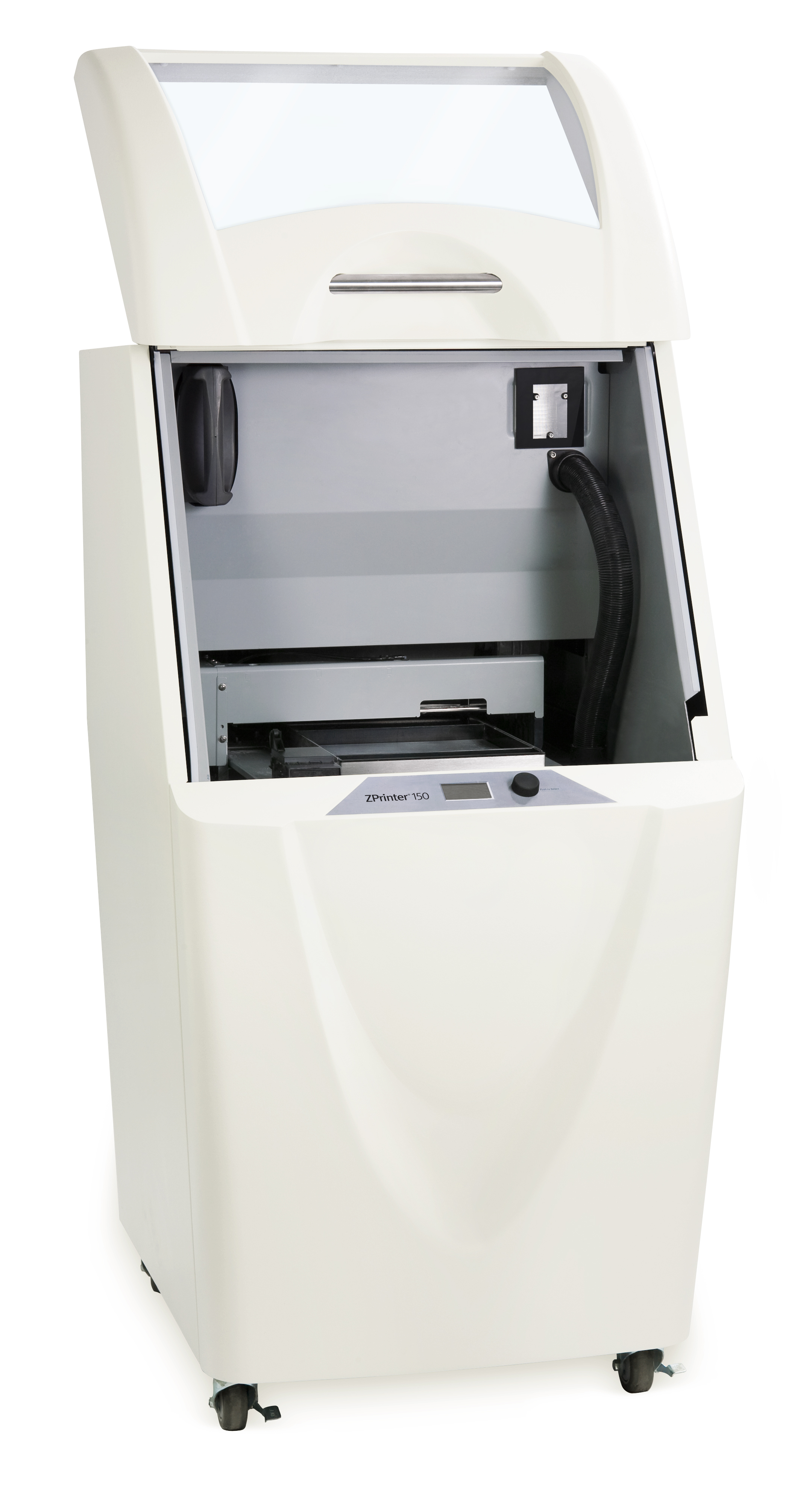

Another approach is chosen powder printing, in which a fine powder is spread over the impress surface, and either a laser sinters (melts) the powder (a process chosen selective laser sintering or SLS), or a solvent liquefies the powder, causing it to bind together to form the layer. The advantage of powder printing is that information technology can support a broad range of materials, including metals, glass and plastics. By mixing dissimilar colors of powder, they are the only printers that tin can create custom-color 3D prints.
MORE: The Future of 3D Printing Materials
However, powder printers are more circuitous to build and need either a powerful laser or a solvent, so they are expensive. The Zprinter 150, for case, is nonetheless a commercial-grade machine and costs $11,000. Patient tinkerers can access the technology more affordably by building their own printer using the open-source design of the experimental pwdr printer.
Pros: The printer can brand objects in multiple, customized colors past mixing different colored powders. Some models can impress from powdered metals.
Cons: Currently, pulverisation printers are either very expensive or only bachelor as open-source designs that you can effort to build yourself. The printing materials are also expensive.
Central Features & Accessories: Equally with all 3D printers, consider the size of the print surface area and the price of printing. If you have to buy the press material from one company (as you lot do with the ZCorp models), you should include this in your calculations, every bit the material is unremarkably pretty expensive.
Of import 3D Printer Features and Specs
Build Surface area: This is the maximum size of an object that the 3D printer tin build. This is usually measured in XYZ dimensions, such as eight inches wide (X) by 8 inches deep (Y) past viii inches high (Z). A smaller build area tin be limiting, but most print jobs can be split into smaller parts that can be combined afterward, and then it may non be quite as limiting as it first appears. In general, look for a build area of at least 5 x 5 x v inches 13 x thirteen x 13 cm), which should be large plenty for nearly printed parts.
Extruders: The extruder is the business organization terminate of filament printers, where the press fabric is melted and extruded to lay down each layer of an object. Most models take a single extruder, which means they can print in only ane material or color at a fourth dimension.
Filament Width: Well-nigh consumer 3D printers use a plastic filament, which is usually sold on 2.2-lb. (1 kilogram) rolls for almost $40 to $60. This is available in ii widths: 1.75 millimeters and iii mm, with well-nigh printers using the 1.75-mm type. (The thickness of the layers that the printer uses is determined by the extruder, not the size of the filament.) With about printers, you can buy and employ filament from any manufacturer. The exceptions are printers from Cubify and Stratasys, which use filament cartridges that you have to buy from the manufacturer, at a slightly college price.
Print Speed: This is the speed at which the extruder tin can move while laying down the print textile for a filament printer. A faster print speed usually ways quicker prints. However, the blazon of material used can too affect the print speed, and the complication of the print tin can also slow down printing: Complex models with lots of edges make for slow prints. You should wait for a pinnacle speed of at least xx mm per 2nd, if possible. Other printer types (such as SLA and SLS printers) don't measure out speed in the aforementioned way.
Horizontal, XY or Feature Resolution: Similar a newspaper printer, 3D printers have minimum resolutions that determine the level of detail they tin produce. The horizontal (or XY) resolution is the smallest movement that the extruder or print head can brand inside a printed layer. A smaller horizontal or XY resolution means more fine detail in prints, then look for a measurement of at to the lowest degree 0.01 inches (0.03 cm).
Vertical Z Resolution or Layer Thickness: This is the minimum thickness of a layer that the 3D printer can lay downwards in ane pass. A larger number for this ways thicker, more obvious layers in the final print, while a small number means smoother, more than realistic prints. Just go along in mind that the process will exist slower, because the printer has to create more layers.
Most printers work with a layer thickness of 0.two or 0.3 mm, merely the ability to create 0.ane mm or smaller layers produces noticeably smoother models. Some printers allow yous to adapt the layer thickness, then you can choose whether to make this merchandise-off.
3D Modeling Software
You tin can download digital files for printing from sites such as Thingiverse and Youmagine. But to customize them or become completely creative and design your own pieces, commencement with a simple, free 3D modeling app. We recommend any of the apps beneath. Give them a look and run across which one works best for you.
- Cubify Sculpt
- 123D Brand
- Zbrush
- SketchUp Make
- Seamless3d
- Wings 3D
- Fine art of Illusion
3D Printing Services
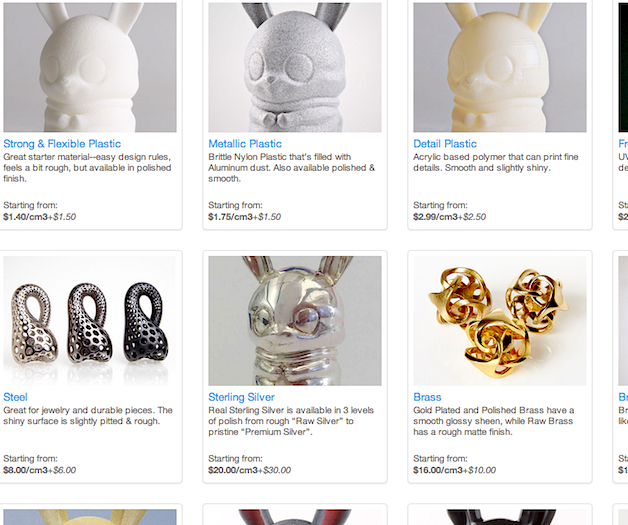
You can get started in 3D press before y'all buy a printer, and without even knowing how to use modeling software. Companies such as Cubify (which besides makes printers), Sculpteo and Shapeways permit you lot to chose designs from their websites, upload models you get from other sites such every bit Thingiverse.com, or upload your own creations for printing on their industrial-course printers. These services offer options to print in materials other than plastic, including ceramic and even metal.

Shapeways
With a streamlined process, a comprehensive range of impress materials and fantabulous customer service, Shapeways is our peak selection.

iMaterialise
The company's piece of cake-to-use Web interface and corking quality are offset by high shipping costs and wearisome delivery.

Sculpteo
Though information technology's not our top pick, Sculpteo offers a potent combo of fast, inexpensive, easy and loftier quality 3D printing.
- Users Rate Best 3D Printers
- MakerBot PrintShop iPad App Is an Intro to 3D Press
- Barbie Rides To Battle on 3D-Printed, Cat-Pulled Chariot
Source: https://www.tomsguide.com/us/3d-printer-buyers-guide,news-17651.html
Posted by: boulangerlosoutypery1946.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How to Buy a 3D Printer"
Post a Comment